The Role of Tokenized Carbon Credits in Supporting Regenerative Ecosystems
7 min read

Table of contents
- Understanding Carbon Offsetting and the Role of Carbon Markets
- The Importance of Tokenization in Carbon Markets
- Enhancing Market Liquidity with Tokenized Carbon Credits
- Exploring Key Tokenized Carbon Pools: BCT, NCT, and NBO
- Stability Mechanisms for Tokenized Carbon Credits
- Conclusion: Tokenized Carbon Credits and the Future of Regenerative Ecosystems
As our world grapples with the urgent need to combat climate change, carbon offsetting has become a vital strategy in the collective pursuit of environmental resilience. However, carbon offsetting must evolve beyond traditional methods to foster regenerative ecosystems. This is where tokenized carbon credits, popularized by initiatives like KlimaDAO and Toucan Protocol, come into play. Tokenized carbon credits bring blockchain technology into the carbon offset market, aiming to make carbon offsetting more efficient, transparent, and accessible. Let’s explore how tokenization has the potential to drive more impactful change in regenerative ecosystems.
Understanding Carbon Offsetting and the Role of Carbon Markets
What is Carbon Offsetting?
Carbon offsetting is the process of compensating for greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by investing in projects that reduce or remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These projects can include reforestation, renewable energy, and other initiatives focused on lowering overall emissions. By purchasing carbon credits, individuals and companies can “offset” their own emissions, supporting projects that contribute to environmental balance and resilience.

Voluntary and Compliance Carbon Markets
Carbon offsetting occurs within two primary types of carbon markets: voluntary carbon markets (VCMs) and compliance carbon markets.
Compliance Carbon Markets: These are government-regulated markets that require businesses and industries to purchase carbon credits to meet specific emission reduction targets. Examples include the EU Emission Trading System (ETS), where entities must adhere to legally binding emission limits.
Voluntary Carbon Markets (VCMs): VCMs allow individuals, organizations, and companies to buy carbon credits voluntarily, primarily to meet corporate social responsibility goals or to demonstrate environmental stewardship.
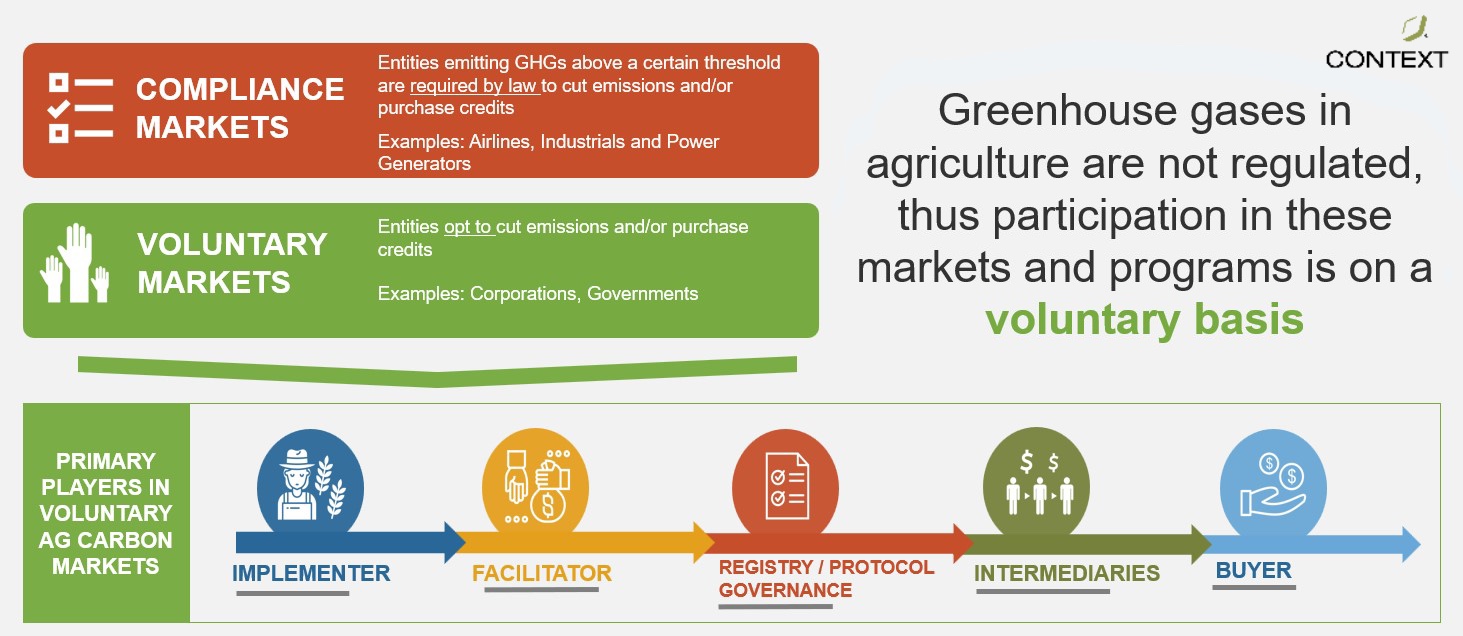
Tokenization is especially impactful within VCMs, enabling new levels of accessibility, efficiency, and transparency for participants.
The Importance of Tokenization in Carbon Markets
Tokenizing carbon credits on blockchain networks provides substantial benefits for both liquidity and accessibility. Here's why tokenization is transformative for the carbon credit market:
a. Creating a Decentralized Market and Liquidity for Carbon Credits
Tokenization enables carbon credits to be traded on decentralized platforms, making them more accessible to individuals and investors outside of traditional exchanges. By using blockchain technology, tokenized carbon credits can be bought, sold, or traded in a private capital market without the constraints of centralized exchanges. This decentralized approach allows anyone with an internet connection to participate in carbon markets, democratizing access and supporting private capital investment in environmental assets.
b. Solving Liquidity Challenges in Carbon Markets
Traditional carbon markets often suffer from liquidity constraints, as different types of carbon credits with unique parameters and project methodologies can be difficult to trade. Tokenized carbon credits, however, solve this issue by allowing diverse credits to be represented as standardized digital assets. By increasing liquidity, tokenization enables a wider range of carbon offset projects to gain market traction, encouraging more sustainable investment options for a diverse audience.
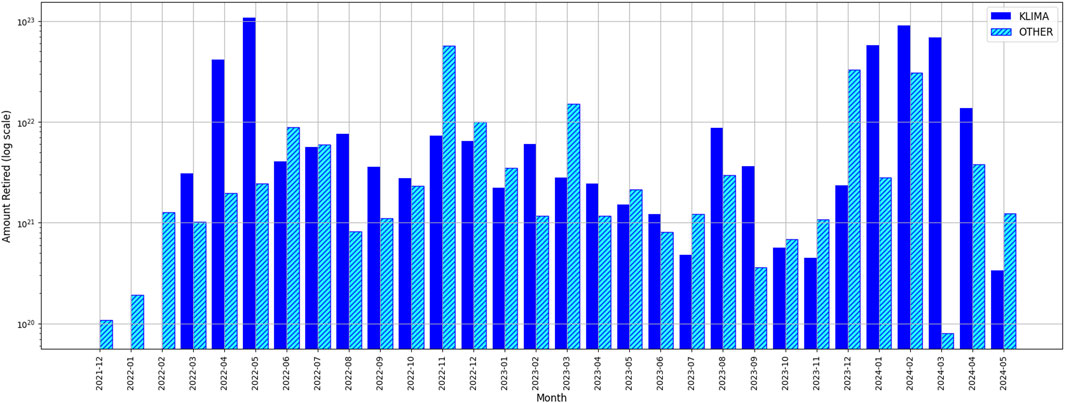
c. Standardization and Transparency in Carbon Credits
Blockchain-based platforms standardize carbon credits into tokens, simplifying the process of trading, buying, and selling. This standardization minimizes transaction friction and ensures transparency, enabling investors to explore a broader range of sustainable projects. As a result, investors gain access to reliable, verifiable carbon credits, fostering a transparent ecosystem in which environmental impact is accurately represented.
d. The Role of KlimaDAO and the KLIMA Token
KlimaDAO has established a unique token, KLIMA, designed to act as a stable asset within the carbon market. Each KLIMA token is backed by a tangible environmental asset—one tonne of carbon offset—sourced from a diverse range of carbon offset projects. This intrinsic value mechanic not only stabilizes the KLIMA token within the carbon market but also bridges digital finance with real-world sustainability.

Through this model, KlimaDAO demonstrates how tokenized carbon credits can support both market stability and environmental impact. By aligning the KLIMA token with tangible assets, KlimaDAO ensures that its token remains a meaningful representation of carbon credits, making it an effective instrument for liquidity provisioning in the carbon market.
Enhancing Market Liquidity with Tokenized Carbon Credits
Liquidity is essential to any efficient market, and it enables seamless trading without large fluctuations in asset prices. Traditional carbon markets, however, are often illiquid and prone to inefficiencies due to their over-the-counter (OTC) structure, where limited visibility on bids and large price spreads can result in price opacity.

By integrating Automated Market Makers (AMMs), KlimaDAO improves the carbon market’s liquidity. With AMMs, such as those popularized by Uniswap, the KLIMA token actively participates in both bidding and asking at narrow price spreads. This structure promotes a transparent, efficient trading environment, ultimately lowering transaction costs and increasing the liquidity of carbon assets. KlimaDAO’s integration of AMMs helps create a fluid carbon market that can scale more effectively, providing a transparent environment for a wide range of stakeholders.
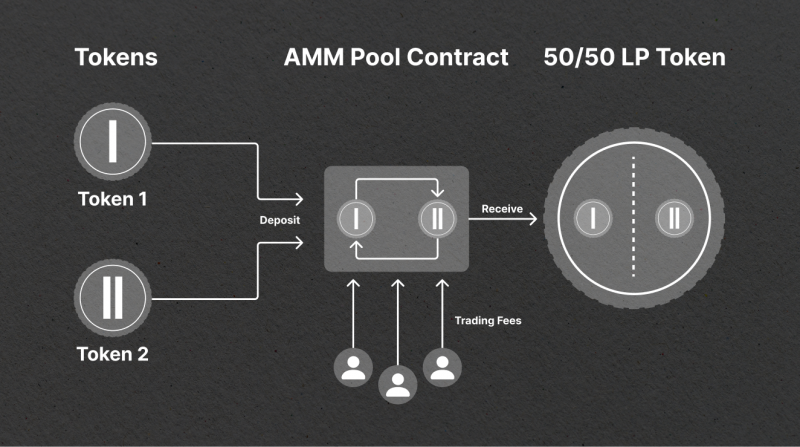
Exploring Key Tokenized Carbon Pools: BCT, NCT, and NBO
Tokenized carbon credits also bring diversity to carbon markets, with each tokenized pool catering to specific ecological needs:
BCT (Base Carbon Tonne): BCT tokens represent a broad range of carbon offset projects with various methodologies, making them a foundational building block for the carbon market. This flexibility makes BCT accessible to a wide variety of projects, enhancing inclusivity and promoting various carbon offset initiatives.

NCT (Nature Carbon Tonne) and NBO (Nature-Based Offsets): NCT and NBO focus exclusively on nature-based projects, such as forestry and land restoration, meeting particular ecological criteria. These pools ensure that the credits represent high-impact, nature-focused solutions, aligning investments with specific environmental goals and contributing to targeted regenerative ecosystem efforts.
Stability Mechanisms for Tokenized Carbon Credits
For tokenized carbon credits to serve as meaningful assets, their value must closely reflect the underlying carbon credit market. If not carefully managed, tokenized carbon credits could experience inflationary or deflationary pressures, impacting their market stability and usability. Therefore, it is crucial to anchor the token's value to real-world carbon credit dynamics, minimizing volatility and maintaining alignment with actual carbon markets.
The Green Ratio: A Strategic Framework for Sustainable Treasury Management
KlimaDAO’s Green Ratio provides an economic framework that guides its treasury allocation to reinforce environmental sustainability. Outlined in KIP-55, the Green Ratio allocates treasury assets into four core categories:
Forward Carbon (22%): Investments in forward carbon contracts, supporting future environmental impact projects.
Treasury Reserves (48%): Assets that bolster KlimaDAO’s financial resilience and ability to engage in market activities.
Operational Expenditure (OpEx, 10%): Funding for operational and developmental needs, ensuring that the DAO can continue to scale and innovate.
Carbon Backing (20%): Carbon offset holdings that underpin the KLIMA token’s intrinsic value, reinforcing the token’s stability in the carbon market.

By adhering to the Green Ratio, KlimaDAO ensures its treasury assets are optimized for both economic resilience and environmental impact, making KLIMA a reliable index for environmental assets.
Conclusion: Tokenized Carbon Credits and the Future of Regenerative Ecosystems
Tokenized carbon credits represent a groundbreaking shift in how we approach environmental sustainability. By integrating blockchain technology with carbon markets, initiatives like KlimaDAO and Toucan Protocol offer a blueprint for decentralized, transparent, and liquid carbon credit markets. These platforms empower individuals and institutions to participate in environmental projects that foster regenerative ecosystems, promoting an interconnected financial model that drives tangible ecological change.
Tokenization, liquidity provisioning, and market transparency are just the beginning. As tokenized carbon credits continue to evolve, they have the potential to become a powerful tool in the fight against climate change, advancing our ability to regenerate ecosystems and create a sustainable future for generations to come.


